Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): a Cognitive Behavioral Approach
By: Jasmyn Cuate
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is a combination of cognitive and behavior therapy, supported by empirical-based evidence that teaches patients skills to cope with and change unhealthy behaviors. The main goals of DBT are to teach people how to live in the moment, develop healthy ways to cope with stress, regulate their emotions, and improve their relationships with others.
DBT focuses on four key areas in therapeutic skills:
- Mindfulness: focuses on improving your ability to accept and be present in the current moment, helping you use healthy coping skills instead of using negative impulsive behaviors
- Distress tolerance: teaches you how to feel intense emotions without reacting impulsively or using self-injury or substance abuse to escape from it. Helping you prepare for intense emotions and cope with a more positive long-term outlook
- Emotion regulation: teaches you how to identify, label, and change your emotions without judging them– learning how your emotions shape your behavior and what obstacles prevent you from managing your emotions, reducing your emotional vulnerability and helps you have more positive emotional experiences
- Interpersonal effectiveness: allows you to communicate more effectively with others, become more assertive, maintain self-respect and respect for others, while keeping a relationship positive and healthy
DBT goes through a multistage approach where the therapist first treats the patient’s most self-destructive behavior followed by the therapist addressing quality-of-life skills, then focus on improving the patient’s relationships and self-esteem, with the last stage focusing on promoting more joy and relationship connections. Standard comprehensive DBT is often used in the following settings:
- Individual therapy: with a trained professional, you learn how to apply DBT skills to specific challenges and situations in your life– patients agree to do homework to practice new skills and fill out diary cards which are completed daily to keep track of their emotions, urges, behaviors, and skills used throughout the week and brought to weekly sessions for the therapist and client to discuss and see if there’s progress being made. Diary cards are designed to record instances of target behaviors, thoughts and urges, and the use of behavioral skills client’s applied to cope with the problem
- Group skills training: patients have the opportunity to role-play new behavioral skills and interact with others
- Phone coaching: with DBT, your therapist is available by the phone for in-the-moment support between sessions if you’re in a difficult situation and need guidance
While your therapist works with you through the DBT approach, it can be challenging to stay motivated. Therefore, therapists have consultation groups,which are a group of professionals who met regularly helping one another to navigate potential stressors, monitor their devotion to treatment, develop and increase their skills, and sustain their motivation to work with high-risk, difficult-to-treat clients.
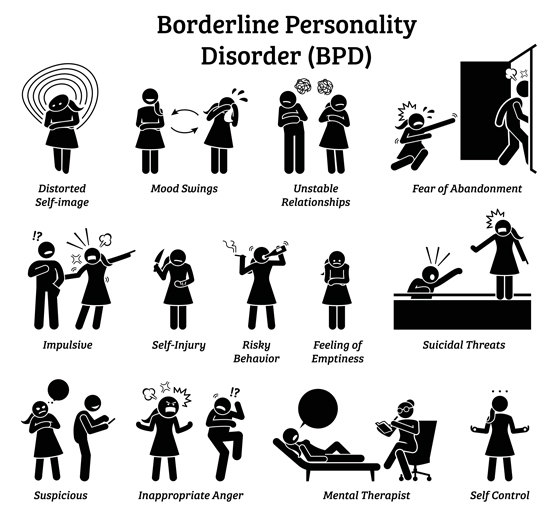
DBT was developed by Marsha Linehan, originally intended to treat borderline personality disorder (BPD) and suicidal behaviors but has been modified to treat other mental health conditions and have been effective in treating:
- Borderline personality disorder (BPD)
- Bipolar disorder
- Substance use or impulsive behaviors
- Eating disorders
- Depression
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Non-suicidal self-injury (NSSI) or suicidal behavior
- Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
- Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
Overall, DBT offers validation for patients, helping them understand their actions within the context of their personal experiences without necessarily agreeing that their actions are the best approach to solving a problem. This helps patients become more likely to cooperate and work towards self-acceptance and change. The best way to find out if DBT is right for you is to talk with a professional. They will evaluate your symptoms, treatment history, and therapy goals to see if DBT is the best treatment option for you.
If you or someone you know is seeking for dialectical behavior therapy, please contact our psychotherapy offices in New York or New Jersey to talk to one of our licensed professional psychologists, psychiatrists, psychiatric nurse practitioners, or psychotherapists at Arista Counseling & Psychotherapy. Contact our Paramus, NJ or Manhattan, NY offices respectively, at (201) 368-3700 or (212) 722-1920 to set up an appointment. For more information, please visit http://www.counselingpsychotherapynjny.com/
Sources: https://www.webmd.com/mental-health/dialectical-behavioral-therapy https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/therapy-types/dialectical-behavior-therapy
https://www.verywellmind.com/dialectical-behavior-therapy-1067402
https://psychcentral.com/lib/an-overview-of-dialectical-behavior-therapy