Borderline Personality Disorder: A Battle Within The Mind
By: Arianna DiRaggio
Personality disorders can often go unnoticed. This is because they are typically difficult to spot and hard to treat. It is very easy to dismiss or look past one’s behavior and simply label it as their personality, never looking more into it. Since it is so difficult to spot, it is important for these individuals to seek help for themselves when the symptoms may be atypical or cause distress.
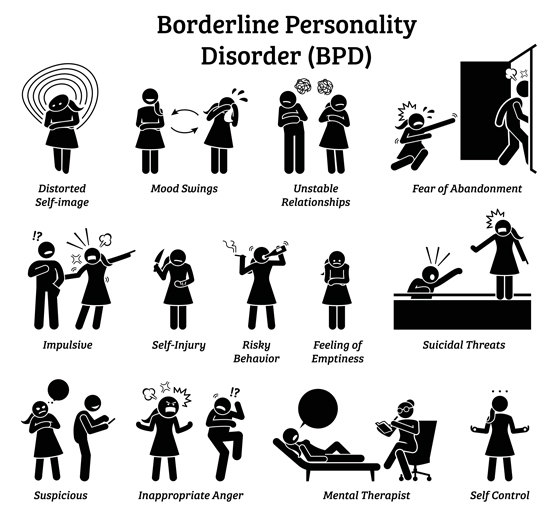
Borderline personality disorder, also known as BPD, is a mental health disorder characterized by instability and impulsivity. This instability and impulsivity often makes it difficult to function in everyday life.
Symptoms of BPD:
- Efforts to avoid real or imagined abandonment
- A pattern of unstable and intense interpersonal relationships
- Persistent and unstable sense of self
- Impulsive behaviors
- Self-harming behavior
- Rapidly changing mood swings
- Feeling like they are “losing touch with reality”
- Difficulty regulating emotional reactions
About 2% of adults are affected by BPD and 75% of those affected are women. Luckily, considerable amounts of research on BPD have been done over the years, allowing us to further understand and assist those struggling with BPD. Different forms of therapy, medications and holistic treatments have all shown positive effects in helping to suppress symptoms.
If you or a loved one is suffering from Borderline Personality Disorder, please contact Arista Counseling & Psychotherapy, located in New York and New Jersey to speak to licensed professional psychologists, psychiatrists, psychiatric nurse practitioners or psychotherapists. To contact the office in Paramus NJ, call (201) 368-3700. To contact the office in Manhattan, call (212) 722-1920. For more information, please visit http://www.counselingpsychotherapynjny.com/ .
Sources:
https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/basics/borderline-personality-disorder