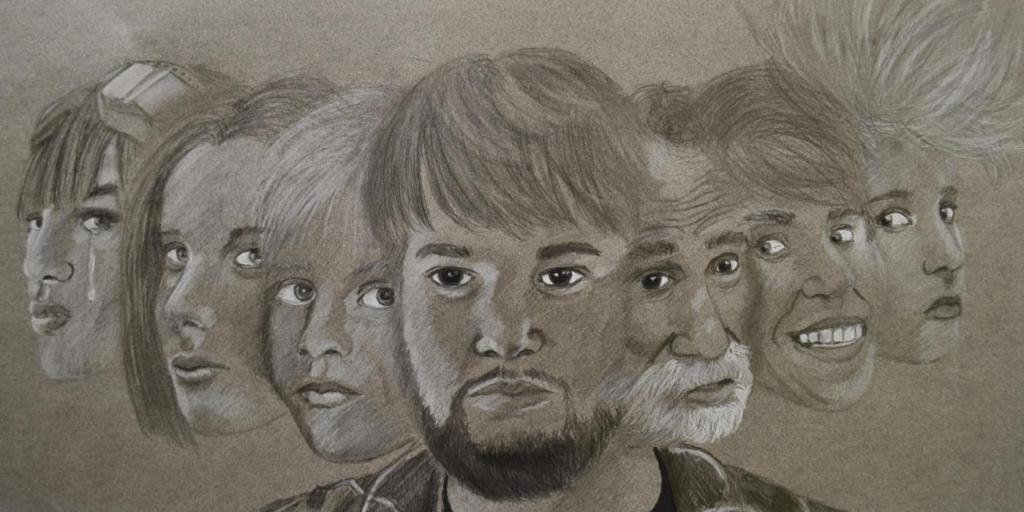
Dissociative Identity Disorder
By: Nicole Staub
Dissociative Identity Disorder, DID, can happen when kids are in a traumatic situation and they don’t quite know how to handle their emotions so the kid dissociates from the situation and their mind essentially “shuts off”. When a kid dissociates, it means that the kid is disconnecting from their thoughts, feelings, and memories. What dissociating may look like is that the kid will “space out”. They will stare blankly at things, look disconnected from the conversation or whatever is going on around them. There can be a sudden shift in their mood or behavior as well. Dissociating looks like the kid is daydreaming. When someone “shuts off” during an incident, they will compartmentalize the experience and how they feel. This is a way of their body protecting themselves from facing the incident at hand. The type of situations a kid might be in could be emotional, physical, or even sexual abuse. Most of the time, Dissociative Identity Disorder forms when you’re an adolescent. There have been examples of DID in movies or TV shows. However, more likely than not, movies and TV shows portray the disorder incorrectly.
Dissociative Identity Disorder can help kids keep their ability to understand humor, have creativity, and reflection. If someone has DID, it could be hard for their family and friends to notice when someone is switching. People rarely see the symptoms if someone is experiencing DID. One of the symptoms someone may have is “memory gaps”. Memory gaps are considered missing memories. What this means is that someone might not be able to recall important events or details that have happened in their lives because they weren’t present for that memory. A different identity was present for that event and will remember it. If the patient doesn’t know they have the disorder, it can be scary for them to have “memory gaps”. Having Dissociative Identity Disorder in your adult life can become more of a problem if the threats of the incidents are no longer there. If you are an adult and are first seeking help for DID, it could be more a difficult recovery process but not impossible.
To get diagnosed with Dissociative Identity Disorder, you need to experience these criteria:
– The presence of two or more distinct identities or personality states.
– At least two of these identities or personality states recurrently take control of the person’s behavior.
– Inability to recall important personal information that is too extensive to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness.
– The disturbance is not due to the direct psychological effects if a substance (blackouts due to alcohol) or a general medical condition (seizures).
This disorder is treatable. Typically, how the treatment goes is that it is done in three phases. Phase one is about the patients’ stability and safety. Make sure that the patient has healthy coping mechanisms in general and if the patient has thoughts about or has harmed themselves or has had suicidal thoughts. Phase two is to identify the traumatic situation, address it and working through the problem. Finally, phase three is for the patient to not rely on dissociating when difficult situations occur.
If you or someone you know is having mental health difficulties and/ or experiencing symptoms of Dissociative Personality Disorder, please contact our psychotherapy offices in New Jersey to talk to one of our licensed professional psychologists, psychiatrists, psychiatric nurse practitioners, or psychotherapists at Arista Counseling & Psychotherapy. Contact our offices at (201) 368-3700 or (212) 722-1920 to set up an appointment. For more information, please visit http://www.counselingpsychotherapynjny.com/
Source
Dissociative identity disorder: What you need to know | McLean hospital. Understanding Dissociative Identity Disorder. (2024, July 6). https://www.mcleanhospital.org/essential/did









