By: Seunghee (Sunny) Rhew
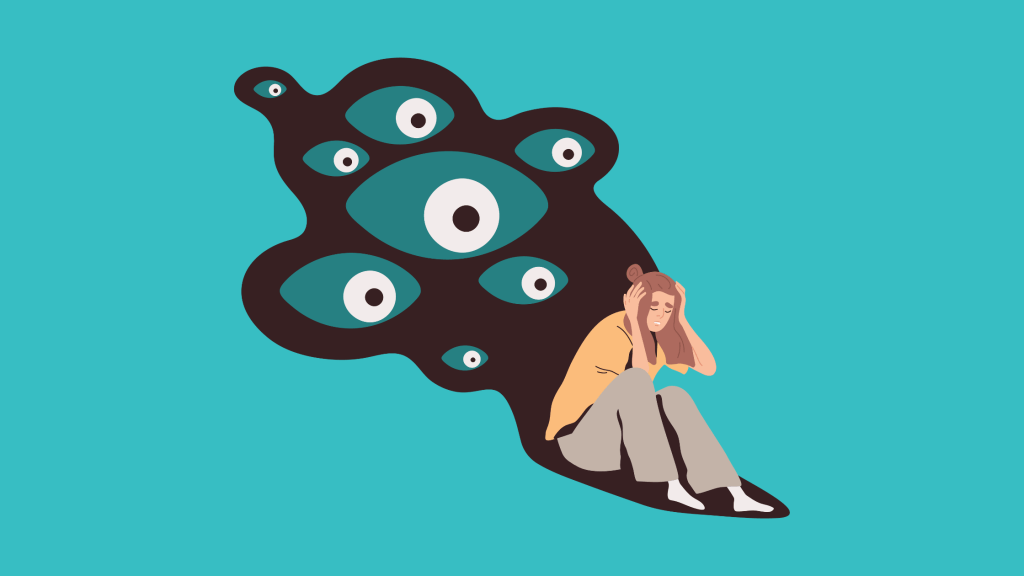
It’s New Year’s Eve. You’re frantically scribbling last-minute resolutions on a scrap of paper, hoping that somehow the clock striking midnight will transform you into a brand-new person with a clean slate. But as you write these big, ambitious goals, a familiar pressure starts to build in your chest. Your mind races: Will I actually be able to do all of this? Am I taking on too much? What if I disappoint myself again?
The questions multiply, pulling you back into memories of the past year—every misstep, every abandoned plan, every moment you felt less than who you wanted to be. Suddenly you’re not just thinking about resolutions anymore. You’re questioning your life choices, your abilities, even your purpose. That’s exactly how anxiety tends to show up: quietly at first, then all at once, flooding your mind with what-ifs and worst-case scenarios.
But the start of a new year doesn’t have to trigger panic or self-doubt. It can be an opportunity to understand your anxiety with more compassion and to build healthier, calmer routines. One of the most effective ways to do that is by practicing mindfulness and grounding—skills that help bring you back into the present moment instead of spiraling into the future or the past!
Some common triggers of anxiety are:
- Health issues
- Negative thinking
- Financial concerns
- Social events
- Conflicts with friends, families, and partners
- Medication
- Not having a significant other
- Skipping meals
- Worries about the future
Some exercises you can do to combat these triggers include…
- 5-4-3-2-1 Method: Identify 5 things you see, 4 you can touch, 3 you hear, 2 you smell, and 1 that you can taste.
- 4-7-8 Breathing Exercise: Breathe in through your nose for 4 counts, hold your breath for 7 counts, and exhale through your mouth for 8 counts.
- Repeat positive statements to yourself: Reciting daily affirmations about yourself might sound like “I am capable,” “I am worthy of love,” “I am safe in this moment,” or “Everything is going to be okay.”
If you or someone you know is struggling with mental health, please contact our psychotherapy offices in New York or New Jersey to talk to one of our licensed professional psychologists, psychiatrists, psychiatric nurse practitioners, or psychotherapists at Arista Counseling and Psychotherapy. Contact our Paramus, NJ, or Manhattan, NY offices respectively, at (201) 368-3700 or (212) 722-1920 to set up an appointment. For more information, please visit https://www.counselingpsychotherapynjny.com/.
Sources:
https://www.calm.com/blog/how-to-be-more-present
https://www.healthline.com/health/anxiety/anxiety-triggers#identifying-triggers









